1 | //将元素插入队列,往满队列里加入元素抛出异常 |
它的超级实现类AbstractQueue仅实现了add、remove和element三个方法,使其更安全。 add方法调用了offer, remove方法调用了poll, element调用了peek:
1 | public boolean add(E e) { |
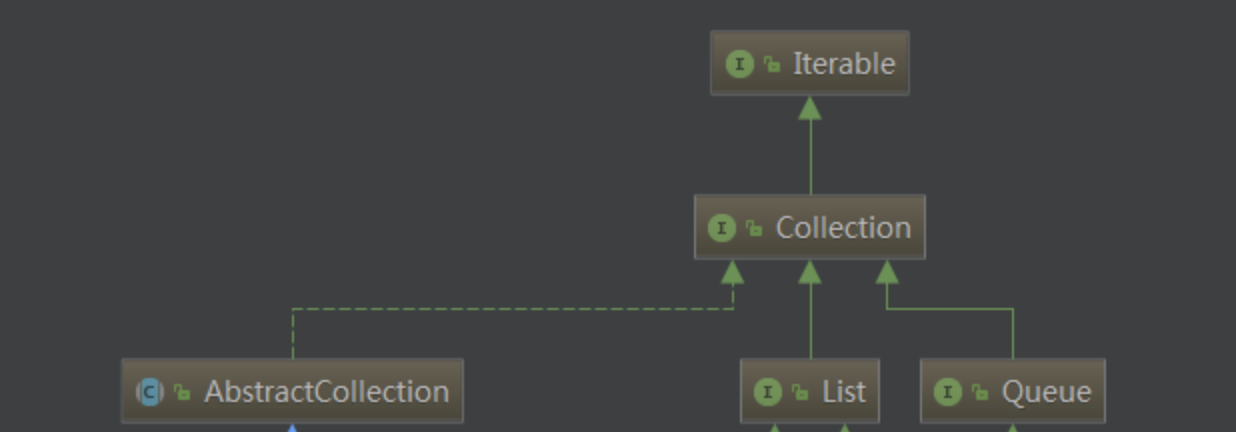
Queue有一个子接口Deque(Double ended queue),双向队列。双向队列允许插队到队头,允许队尾离开。同时它实现了stack
1 | //与addFirst()等价 |
Queue实现类ArrayDeque
可动态调整大小的数组来实现了Deque,和ArrayList有点相似,但实现不同。ArrayDeque的动态大小总是2的次幂,而不是每次增长1.5倍。
成员变量
1 | //存放元素,长度和capacity一致,并且总是2的次幂 |
##构造函数
1 | //无参,默认大小16 |
在定义elements变量时说,其长度总是2的次幂,但用户传入的参数并不一定符合规则,所以就需要根据用户的输入,找到比它大的最近的2次幂。比如用户输入13,就把它调整为16,输入31,就调整为32,calculateSize就是完成了这样一个计算,位运算的代码解析可以看这个链接:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1c1c3f24762e。这个方法让我们找到合适的2次幂。
|按位或
>>> 忽略符号位右移
方法
循环数组,添加元素,在队尾添加,在队头添加,位运算,
1 | //在队首添加一个元素,非空 |
&:按位与。两个数相与,只有都为1的时候才是1,一个正数m和一个数n与得m mod n,和-数与相当于取补码,所以说这个数组实际上是个循环队列。
队列满的情况就是tail == head,这时的扩容策略时直接翻倍。