ArrayList查找性能优秀,但是增删较慢,LinkedList则相反。
LinkedList既实现了List又实现了queue,它的内部实现是一个双向链表。
继承关系
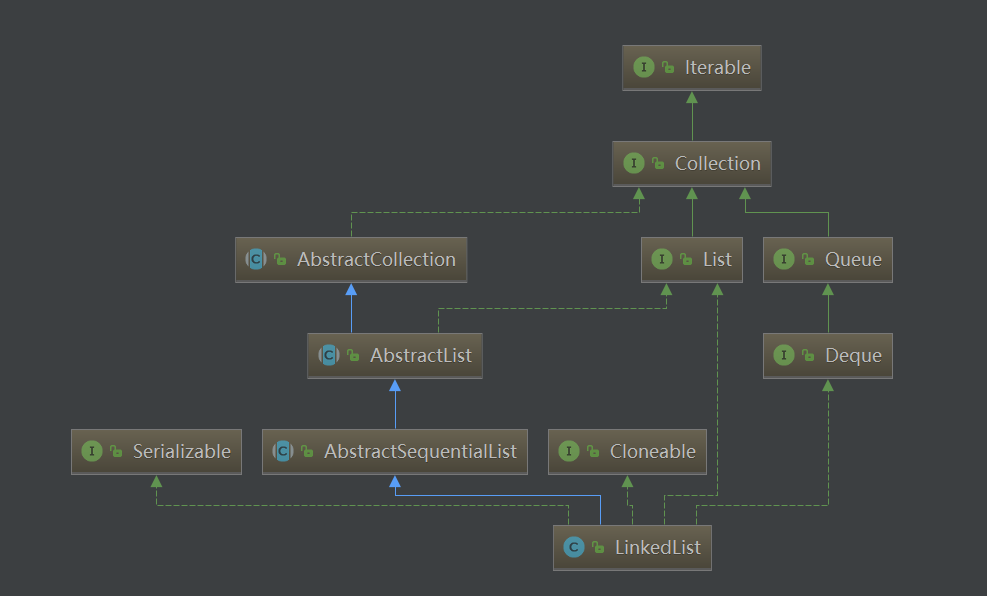
可以看到它继承于List 和 Deque
1 | public class LinkedList<E> |
成员变量
链表大小,头指针,尾指针1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev; //双向
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
构造函数
无参构造函数:一个空链表,只有为null的头尾指针,size=0
有参构造函数:从一个集合构造链表。其中this()可以用来调用当前类的构造函数。然后将集合加入liste。
其中取某个index的节点的代码判断了当前的节点在链表的前半段还是后半段,来决定从头节点开始遍历还是从尾节点开始遍历。二分之一运算用位运算做,速度快省内存效率高(如8*2在底层是用加法实现的,还要判断进位溢出等)。这个方法提高了链表查询的效率。
1 | public LinkedList() { |
方法
1 | //将某节点拼接在链表头部 |
队列的实现:
1 | public E peek() { |
栈的实现:
1 | //从头部加入从头部删除 |
迭代器
1 | public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { |
总结
LinkedList非常适合大量数据的插入与删除,但其对处于中间位置的元素,无论是增删还是改查都需要折半遍历(找到要插入位置的节点),这在数据量大时会十分影响性能。在使用时,尽量不要涉及查询与在中间插入数据,另外如果要遍历,也最好使用foreach,也就是Iterator提供的方式。
ArrayList适合查询,不适合大量的增删操作,LinkedList适合数据的插入和删除(非中间位置),查找性能较差,LinkedList同时实现了队列和栈。Deque是一个双端循环队列。
LinkedList(链表实现)和ArrayDeque(数组实现)都可以用来实现队列和栈,ArrayDeque是推荐的实现队列和栈的方法,效率较高,因为在确定了插入或删除位置时,ArrayDeque的插入或删除是O(1).ArrayDeque是非线程安全的,需要程序员来保证安全。